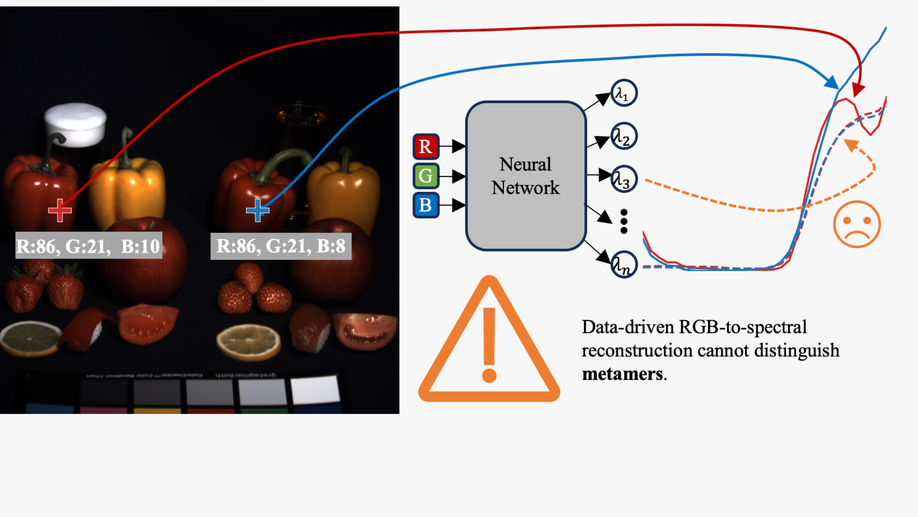
Limitations of hyperspectral imaging from RGB images: An optics-aware analysis
We systematically analyze data-driven spectral reconstruction from RGB images and show that fundamental limitations exist arising from the lack of metamerism and diversity in the existing hyperspectral image datasets.
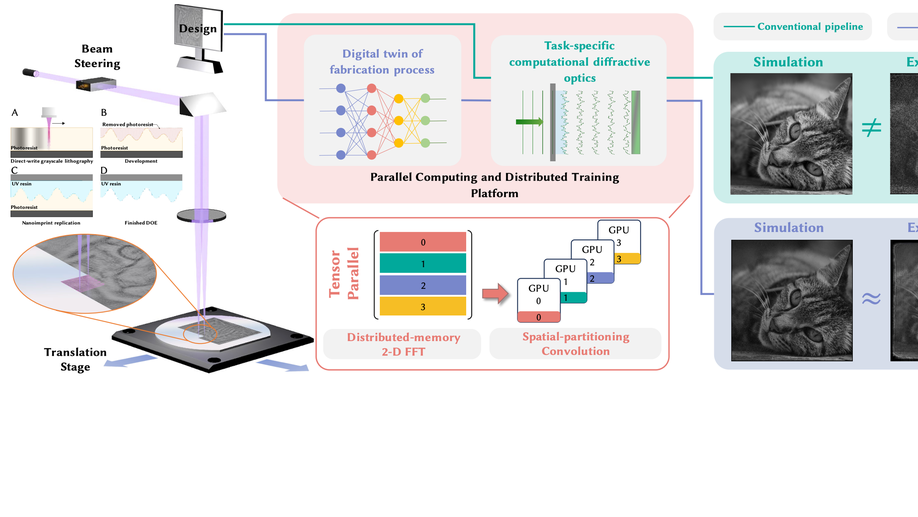
Large-area fabrication-aware computational diffractive optics computational diffractive optics
We propose a fabrication-aware design pipeline for diffractive optics fabricated by direct-write grayscale lithography followed by nano-imprinting replication
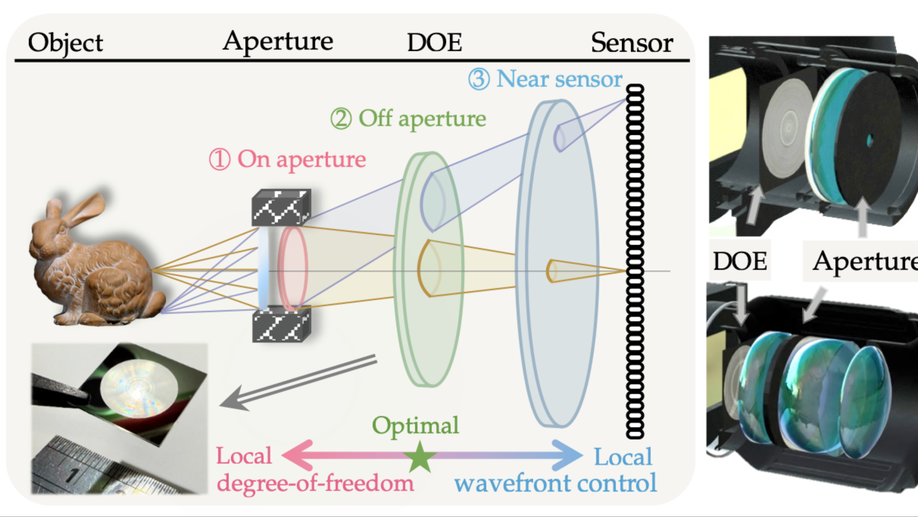
Learned Off-aperture Encoding for Wide Field-of-view RGBD Imaging
We propose a hybrid lens design by positioning a DOE off-aperture to optimize image quality for large field-of-view.
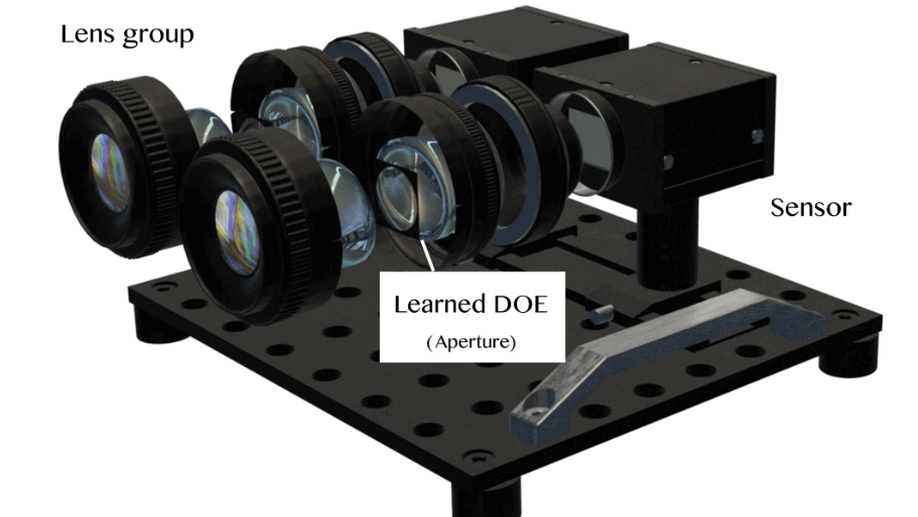
Learned Binocular-Encoding Optics for RGBD Imaging Using Joint Stereo and Focus Cues
We presents a hardware-software co-designed RGBD imaging framework to reconstruct texture-rich color images along with detailed depth maps over a wide depth range.
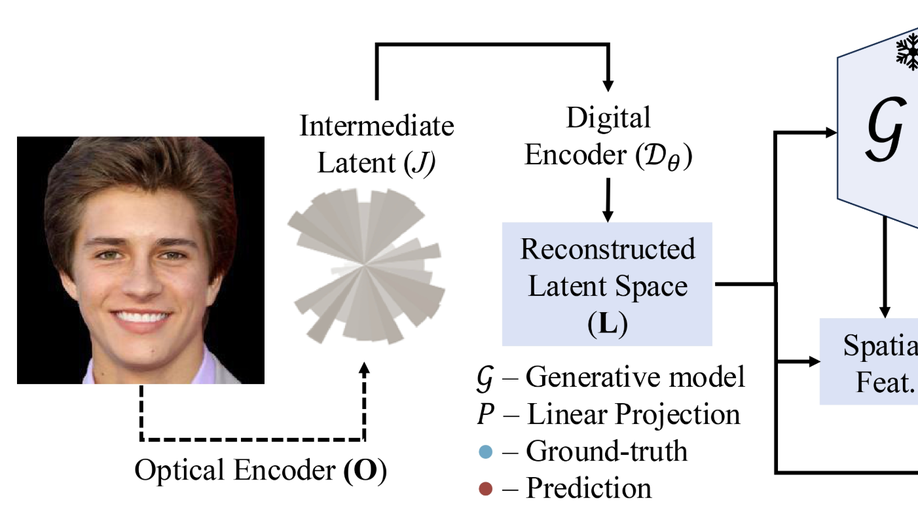
Latent Space Imaging
We introduce a new paradigm that combines optics and software to encode image information directly into the semantically rich latent space of a generative model.
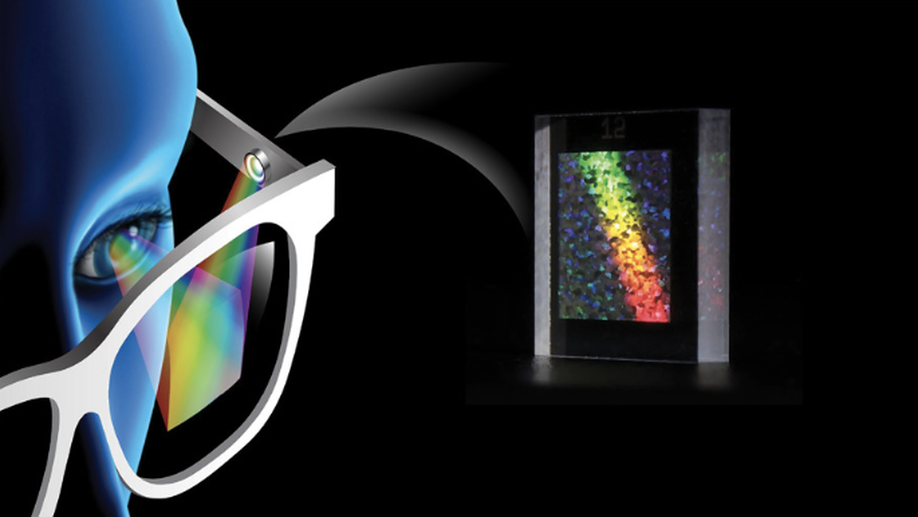

Ultra-Wide-Angle High-Fidelity Holographic Displays
We introduced a fully automated lens design algorithm that uses deep optics and differentiable ray tracing.
An AI Curriculum for Learning Lens Design
We introduced a fully automated lens design algorithm that uses deep optics and differentiable ray tracing.

End-to-end hybrid refractive-diffractive lens design with differentiable ray-wave model
We propose a new hybrid ray-tracing and wave-propagation (ray-wave) model for accurate simulation of both optical aberrations and diffractive phase modulation.
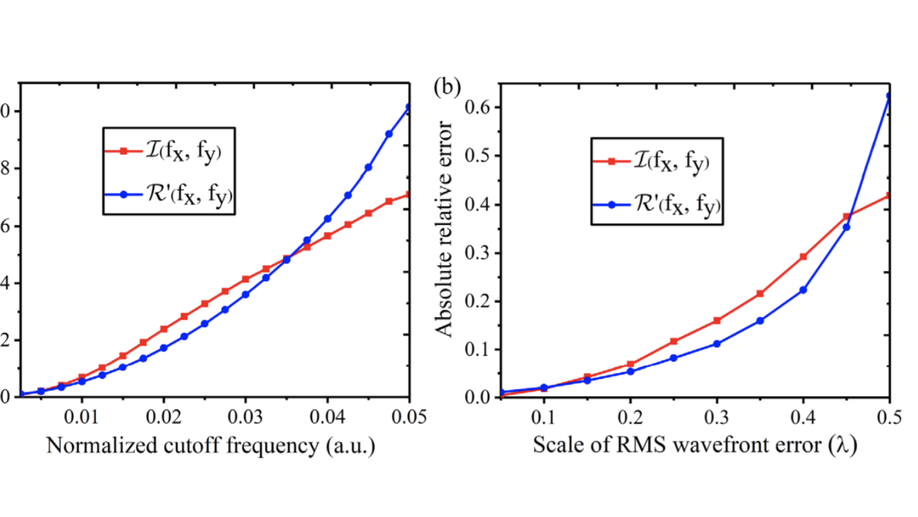
Linearized wavefront sensing model for aberration retrieval from low-frequency Fourier coefficients
We propose and demonstrate a linearized model for phase diversity wavefront sensing, facilitating real-time processing and much less data required for training.
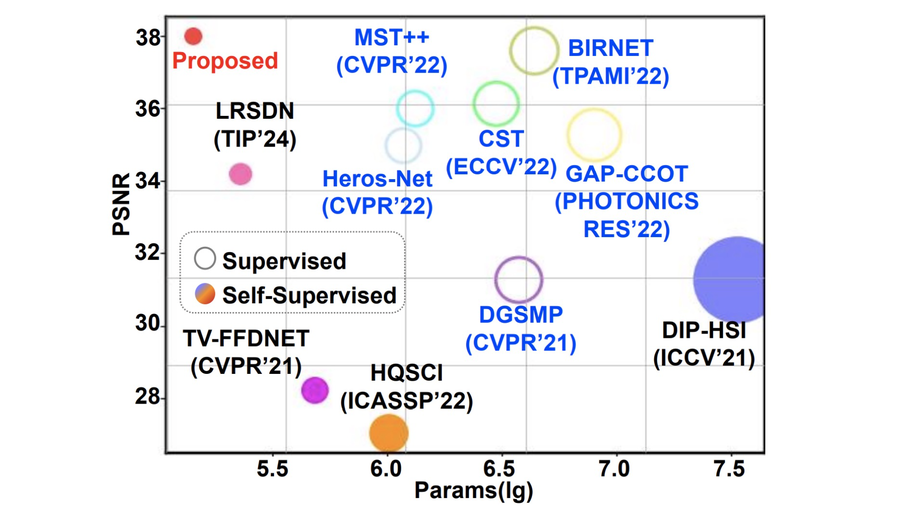
Progressive self-supervised learning for CASSI computational spectral cameras
We propose a self-supervised method tailored for coded aperture snapshot spectral imaging (CASSI).
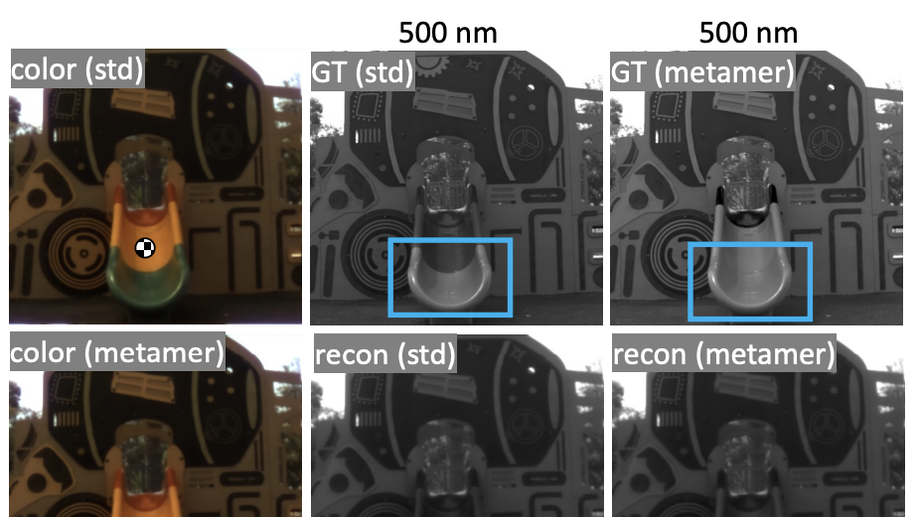
Limitations of hyperspectral imaging from RGB images: A data perspective
We show that significant limitations exist arising from the lack of diversity in the prevailing hyperspectral image datasets.
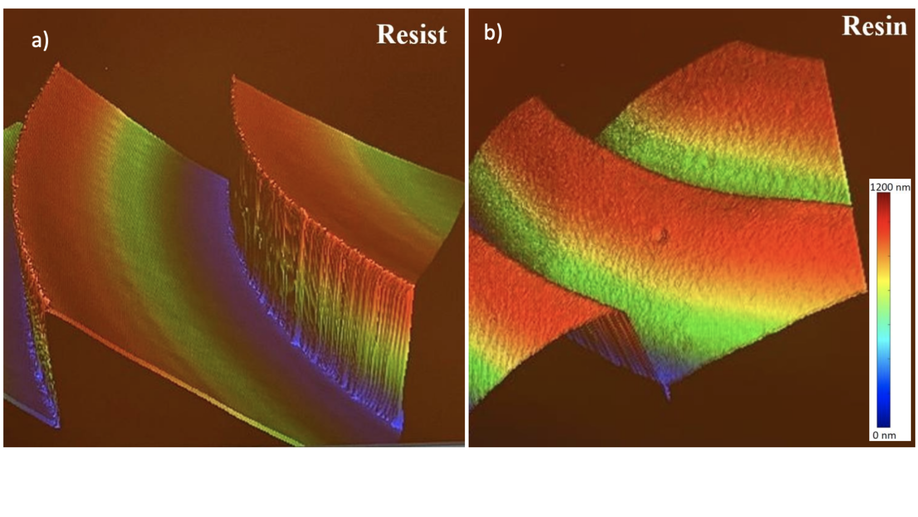
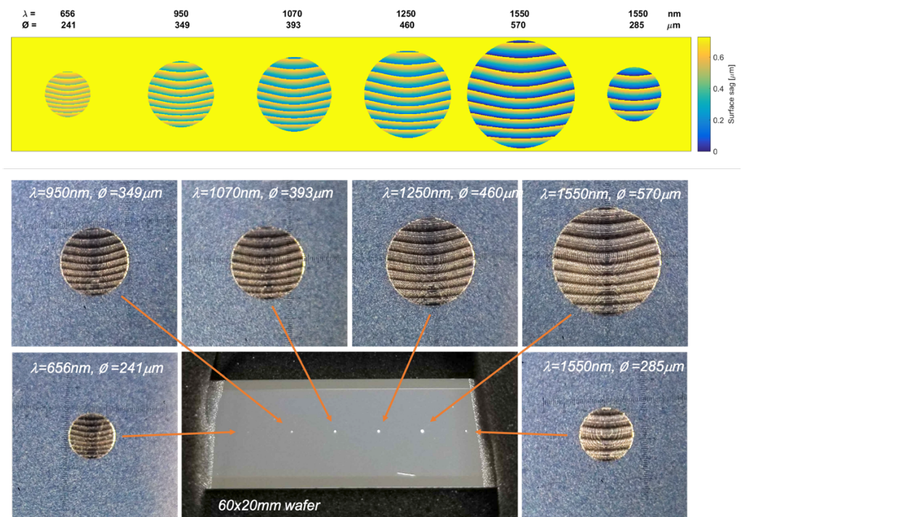
Comparative performance analysis of multi-level diffractive lens and lens fabricated by grayscale lithography and soft-imprinting
We propose a comparative analysis of DOEs fabricated by multi-level photolithography and grayscale lithography.
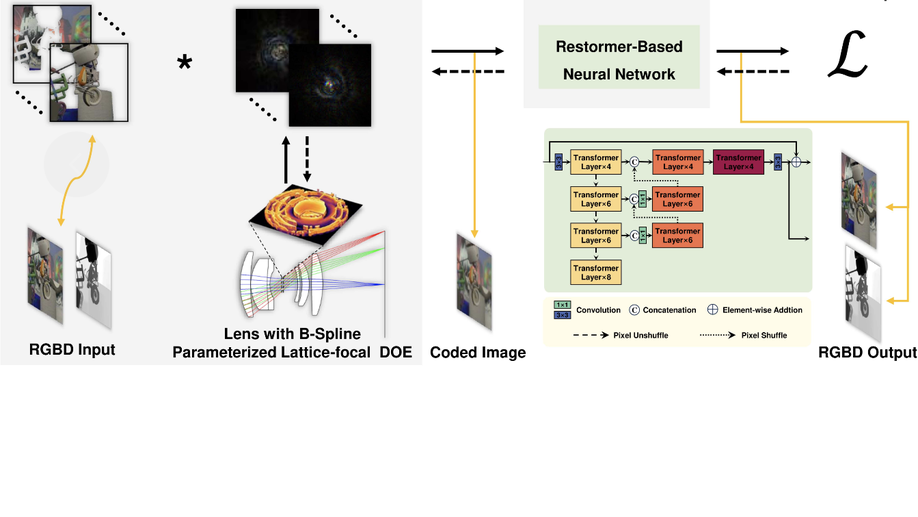
Learned B-spline parametrization of lattice focal coding for monocular RGBD imaging
We employ B-spline parameterization for the DOE surface geometry representation for RGBD imaging.
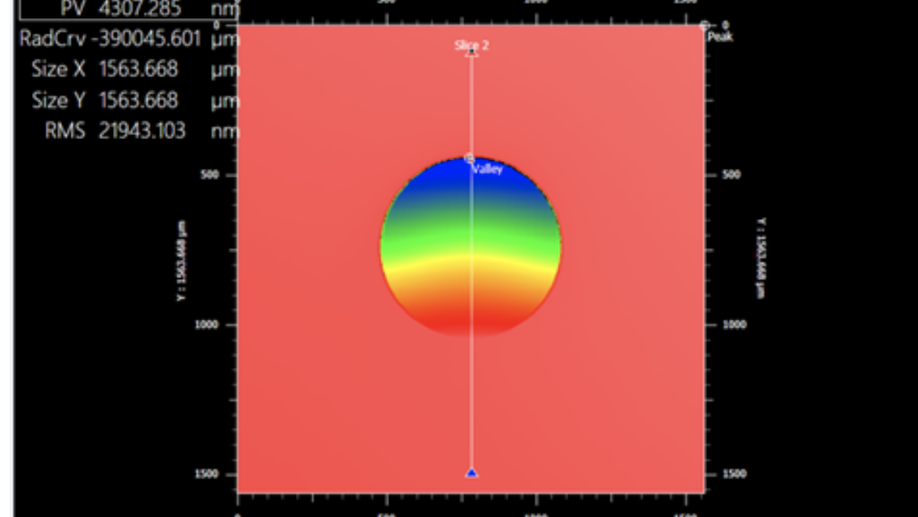
CAL2: project update of the NRC Canada facility-class focal plane wavefront sensor for the Gemini Planet Imager 2 upgrade
The CAL2 project is being built for the GPI calibration system.
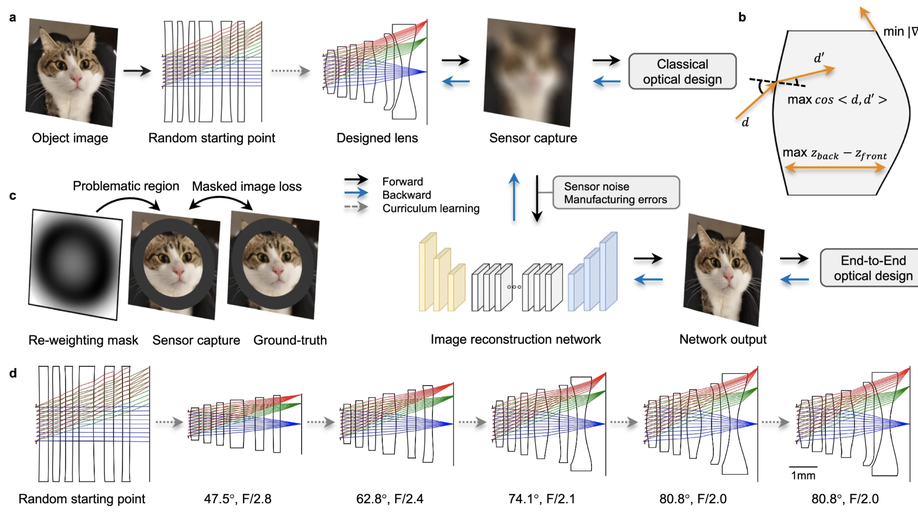
Curriculum learning for ab initio deep learned refractive optics
We present DeepLens, a method to learn optical designs of compound lenses ab initio from randomly initialized surfaces without human intervention.
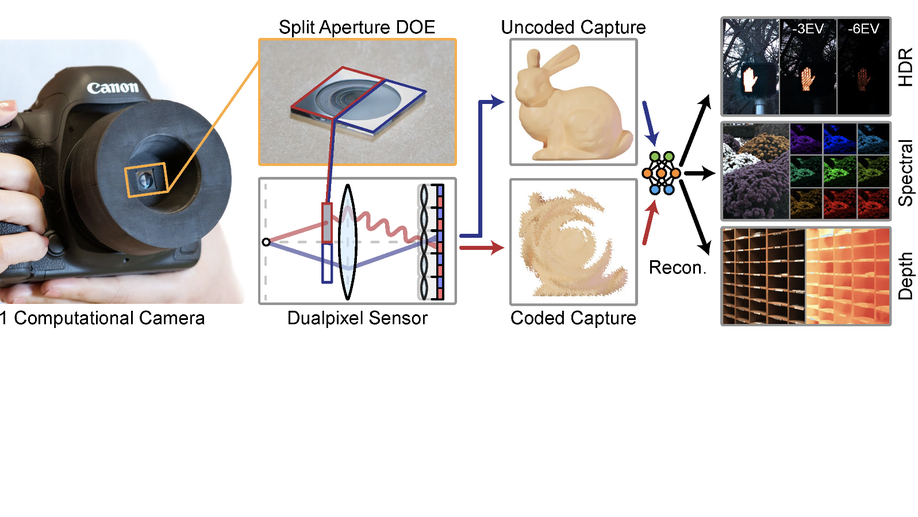
Split-aperture 2-in-1 computational cameras
We propose a method to split conventional camera apertures into two halves along with a dual-pixel sensor for various computational imaging applications.
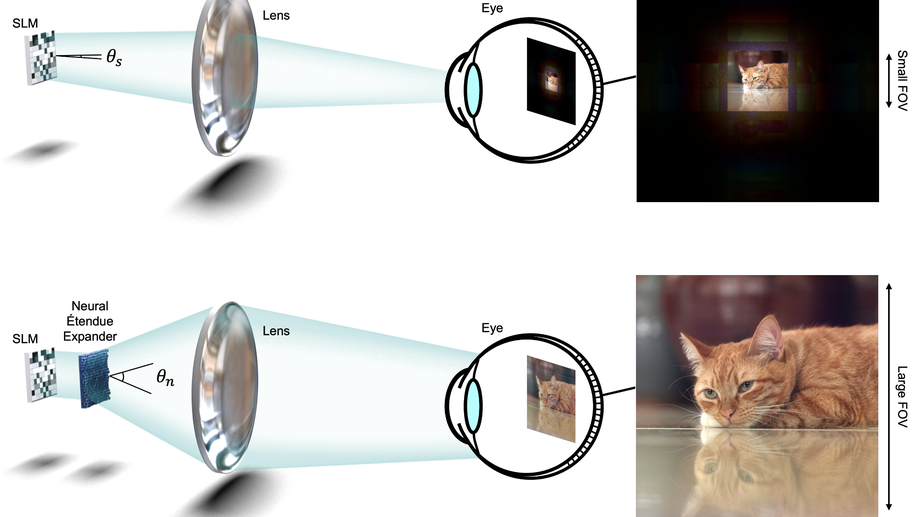
Neural Étendue expander for ultra-wide-angle high-fidelity holographic display
We present a method to expand the étendue of holographic displays by 64x with a learned diffractive optical element.
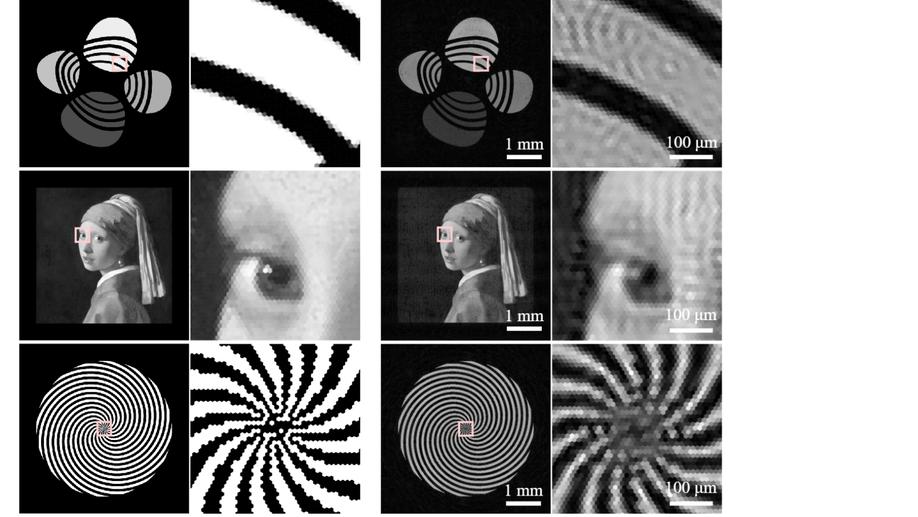
Hexagonal diffractive optical elements
We explore the use of hexagonal grids as a new grid structure for DOE design and fabrication.
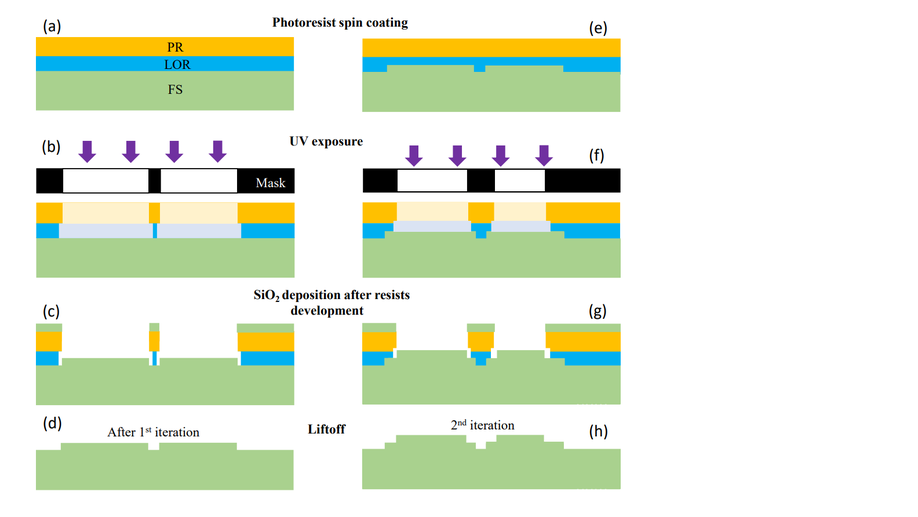
Additive fabrication of SiO2-based micro-optics with lag-free depth and reduced roughness
We propose an alternative method for fabricating DOEs without RIE lag and with improved surface smoothness.
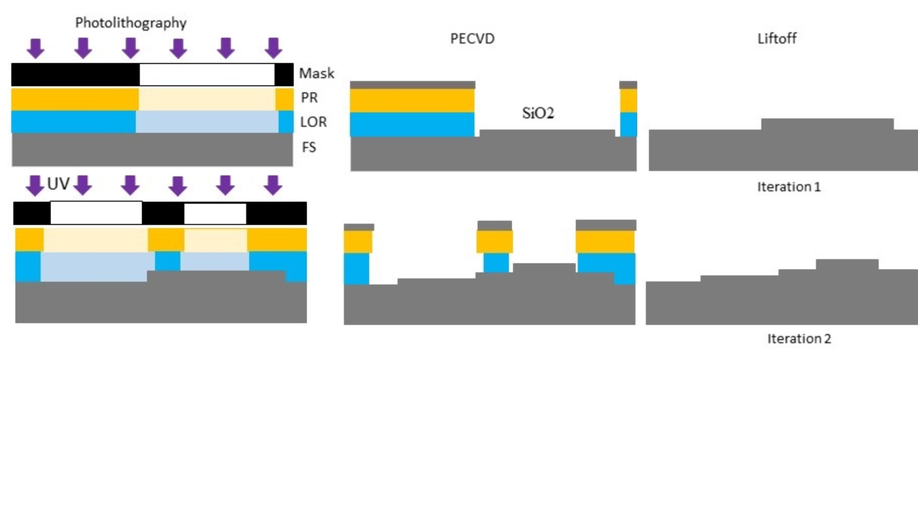
Additive diffractive optical elements fabrication by PECVP deposition of SiO2 and lift-off process
We propose a new way to fabricate multi-level DOEs by directly growing an optically transparent material on a glass substrate.
Aberration-aware depth-from-focus
We explore bridging the gap between aberrations and depth-from-focus through aberration-aware training (AAT).
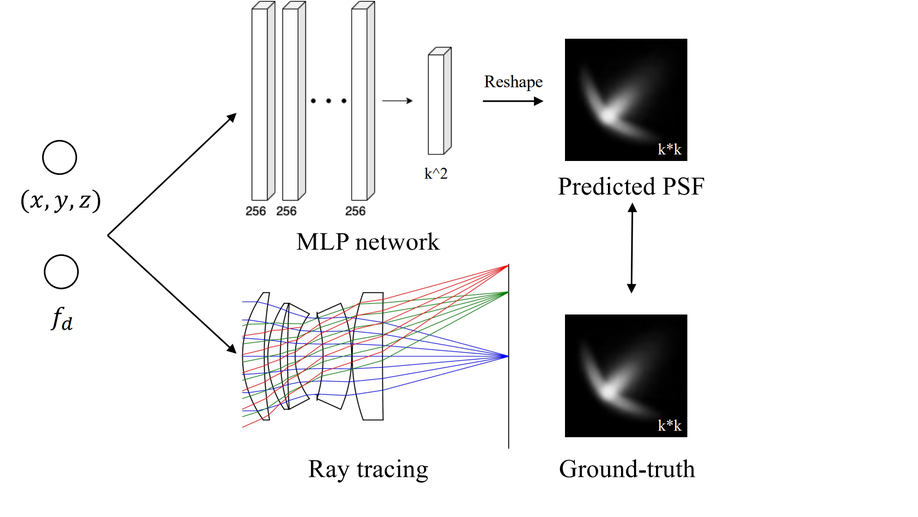
Generalization of learned Fourier-based phase-diversity wavefront sensing
We propose a generalized Fourier-based PDWS method by combining an object-independent network with a system-independent image processing procedure.

Extended Depth-of-Field Projector using Learned Diffractive Optics
We propose an end-to-end joint optimization method to learn a DOE placed in front of a projector lens and a compensation network for deblurring.
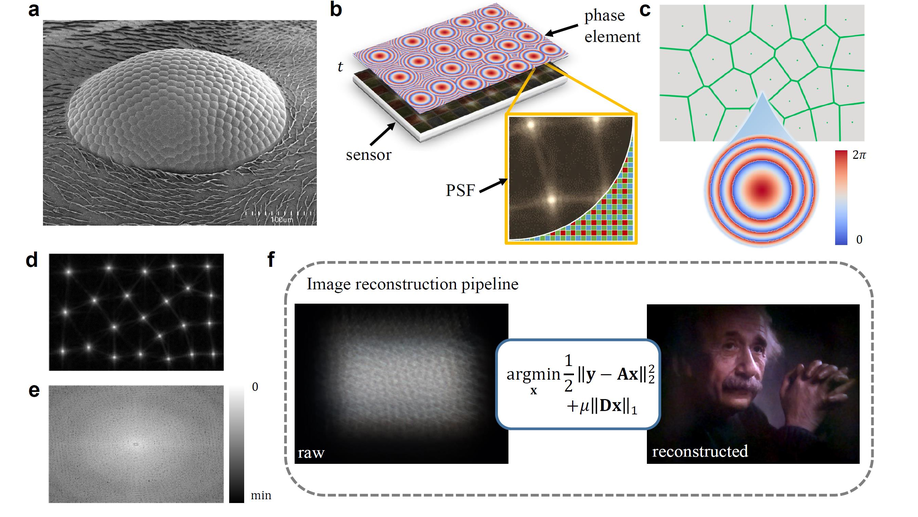
Diffractive lensless imaging with optimized Voronoi-Fresnel phase
We propose a lensless camera with an optimized Voronoi-Fresnel phase by maximizing the Modulation Transfer Function volume.
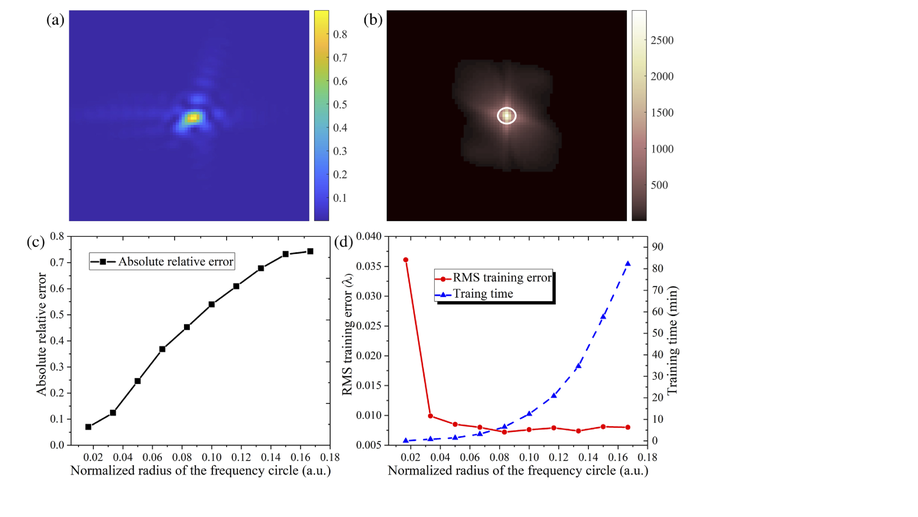
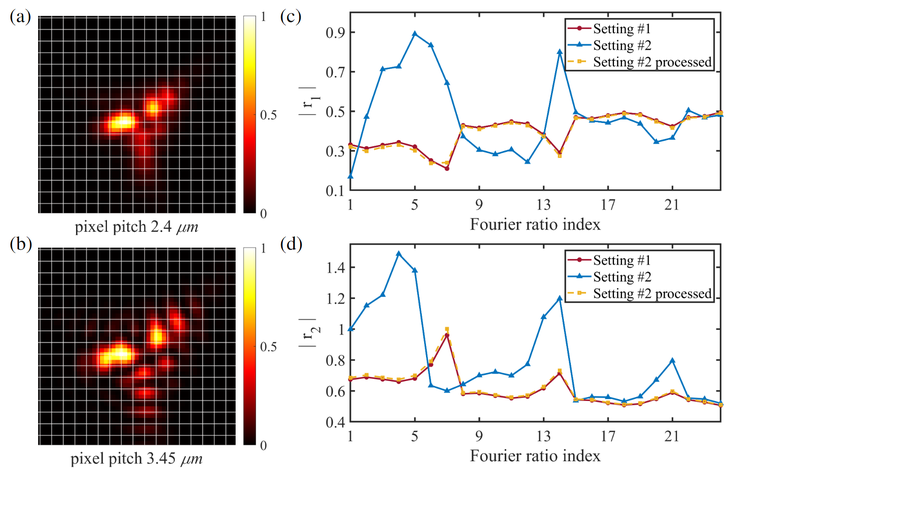
Phase-diversity wavefront sensing enhanced by a Fourier-based neural network
We propose an effective neural network based on low-frequency coefficients in the Fourier domain to determine a better estimate of the unknown aberrations.
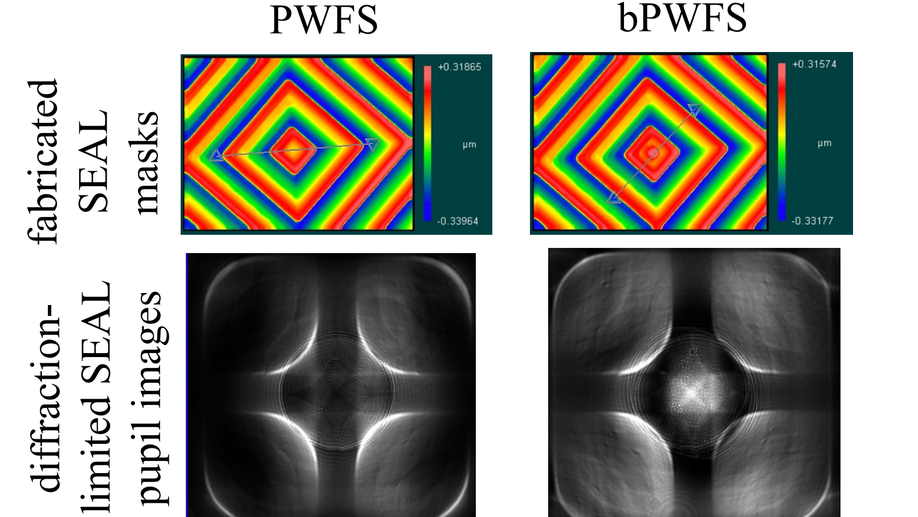
Various wavefront sensing and control developments on the Santa Cruz extreme AO laboratory (SEAL) testbedh
We present three different ongoing wavefront sensing and control project developments on the Santa cruz Extreme AO Laboratory (SEAL) testbed.
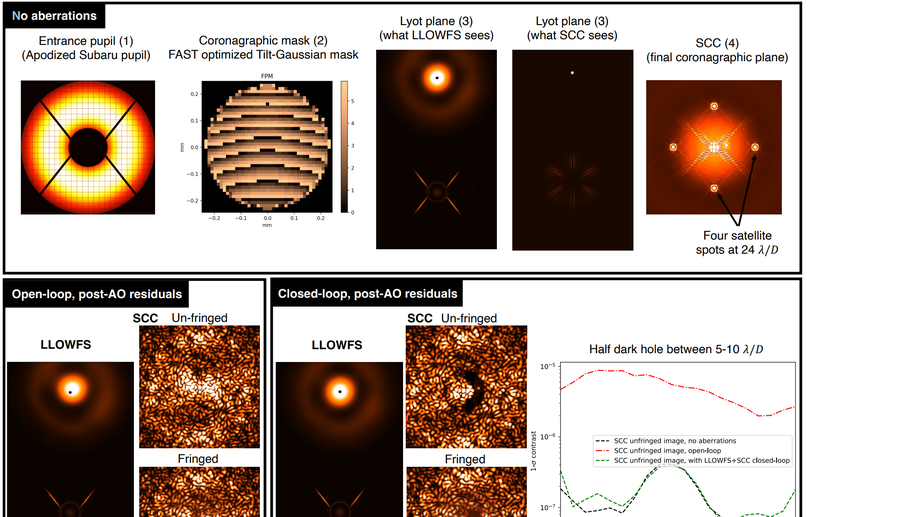
Pupil-plane LLOWFS simulation and laboratory results from NEW-EARTH’s high-contrast imaging testbed
We present LLOWFS closed-loop laboratory results under simulated post-Adaptive Optics residuals of GPI 2.0 and simulations of the LLOWFS and FAST sensors for SPIDERS
Performance of the FAST self coherent camera at the NEW-EARTH lab and a simplified SCC measurement algorithm
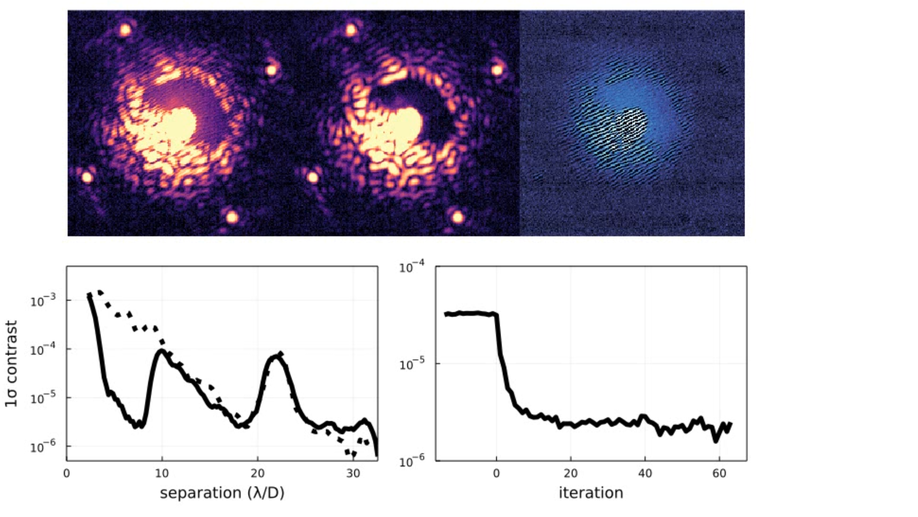
We present here results from NRC’s NEW-EARTH lab testing of the Fast Atmospheric SCC Technique, a variant of the SCC and its integration with a Lyot-stop Low-Order Wavefront Sensor.
Optical design of SPIDERS, a Subaru Pathfinder Instrument for Detecting Exoplanets and Retrieving Spectra
SPIDERS optical design is fully reflective up to the FPM to avoid chromatic aberrations and reduce the number of surfaces.
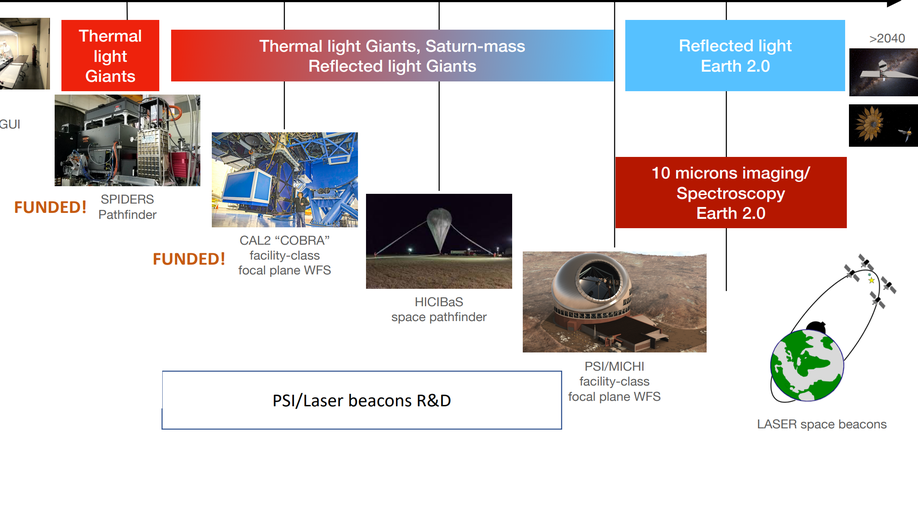
Deployment of focal plane WFS technologies on 8-m telescopes: from the Subaru SPIDERS pathfinder, to the facility-class GPI 2.0 CAL2 system
The NRC Canada is funding two projects, the SPIDERS pathfinder at the Subaru telescope (ETA 2023), and the CAL2 upgrade of the Gemini Planet Imager-2 (ETA 2024), to deploy a modified self-coherent camera (based on FAST) to measure the focal plane electric field, and to apply wavefront corrections in a closed-loop down to 10s of ms in a narrow band.
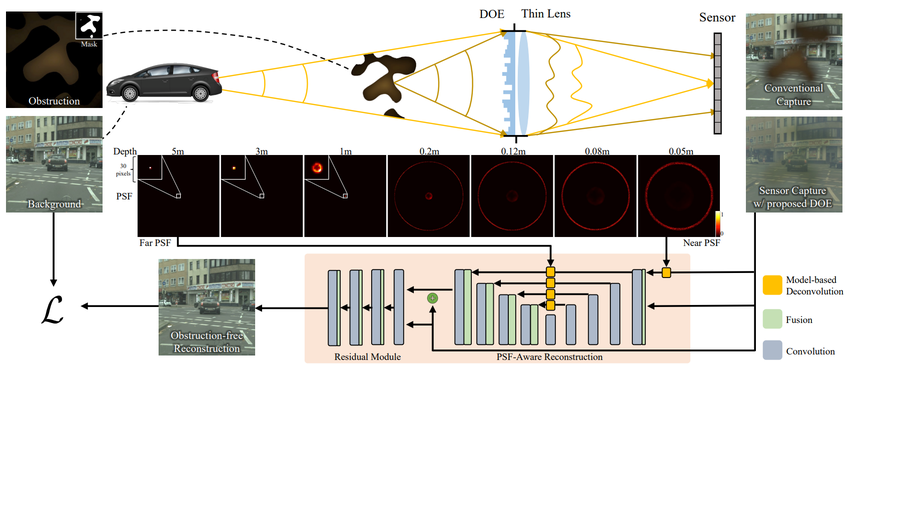
Seeing through obstructions with diffractive cloaking
We propose a monocular single-shot imaging approach that optically cloaks obstructions by emulating a large array.
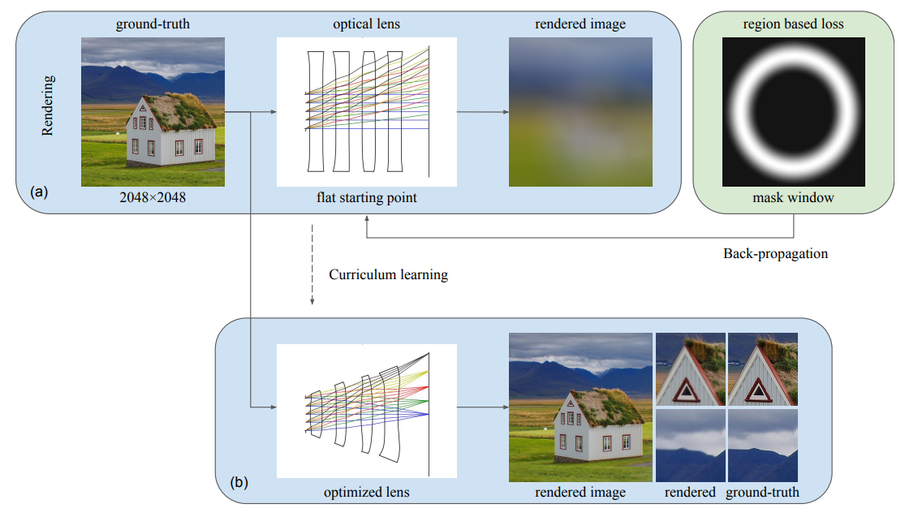
Automatic lens design based on differentiable ray-tracing
We propose a fully differentiable optical design method for lens design.
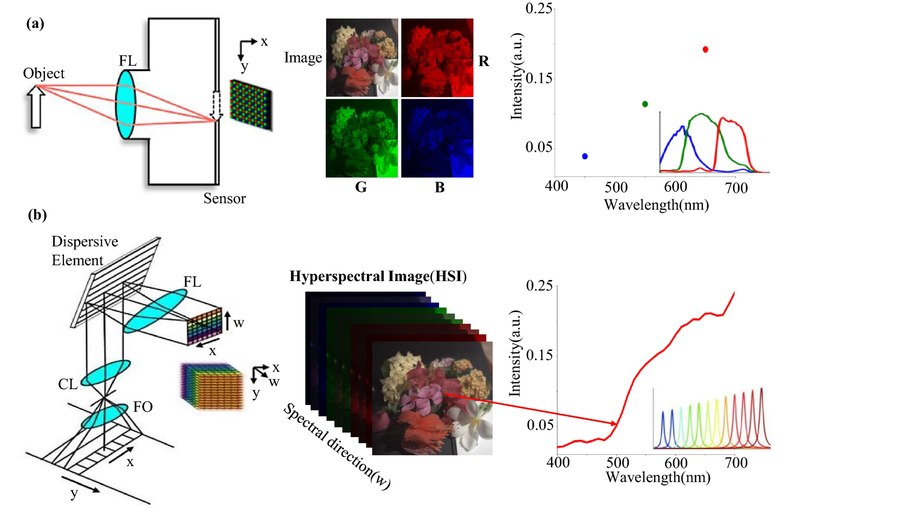
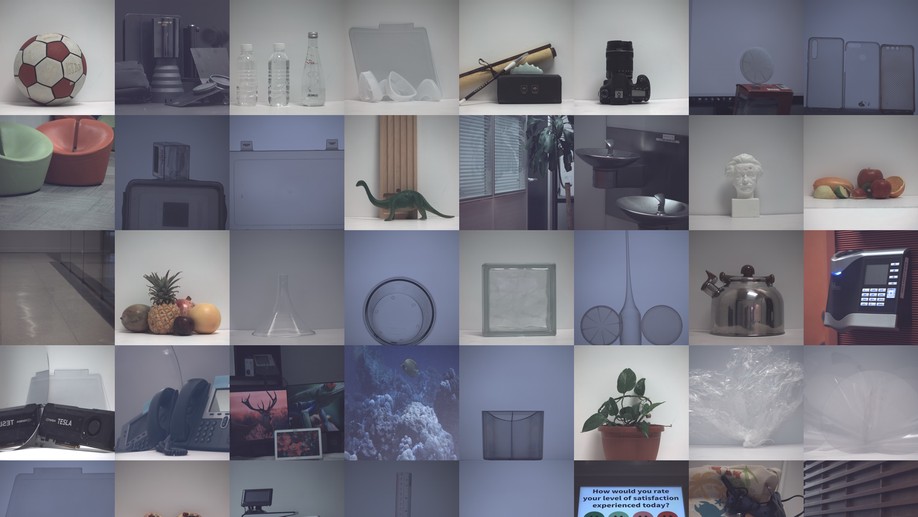
A survey on computational spectral reconstruction methods from RGB to hyperspectral imaging
We present a thorough investigation of more than 25 state-of-the-art spectral reconstruction methods.
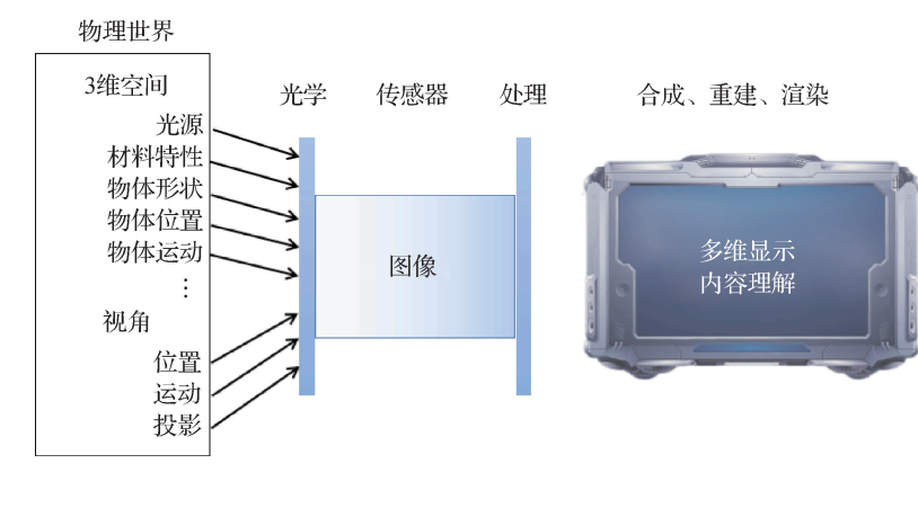
Recent progress in computational imaging
This review reports the latest methods, algorithms, and applications in computational imaging.
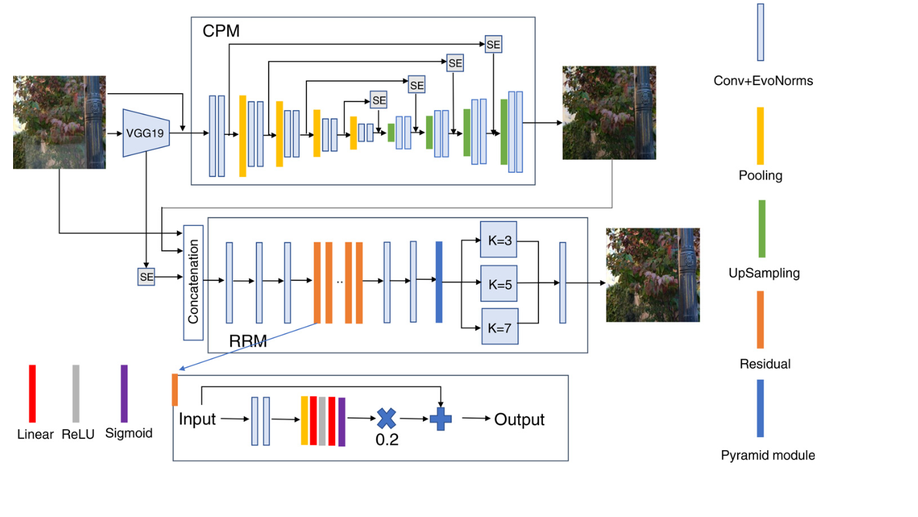
Progressive polarization based reflection removal via realistic training data generation
We introduce a new dataset synthesis method as well as a novel neural network architecture for single image reflection removal.
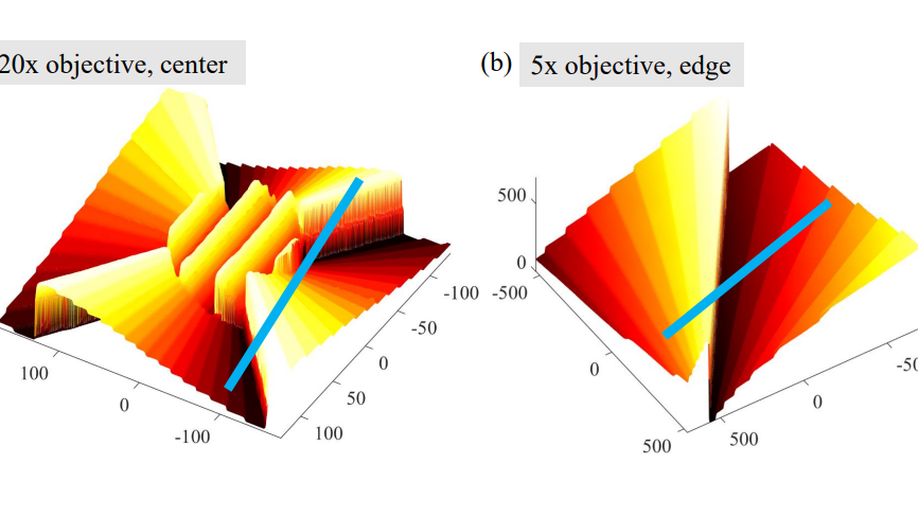
Additive lithographic fabrication of a Tilt-Gaussian-Vortex mask for focal plane wavefront sensing
We propose an additive lithographic fabrication process to realize simultaneous micrometer and millimeter features.
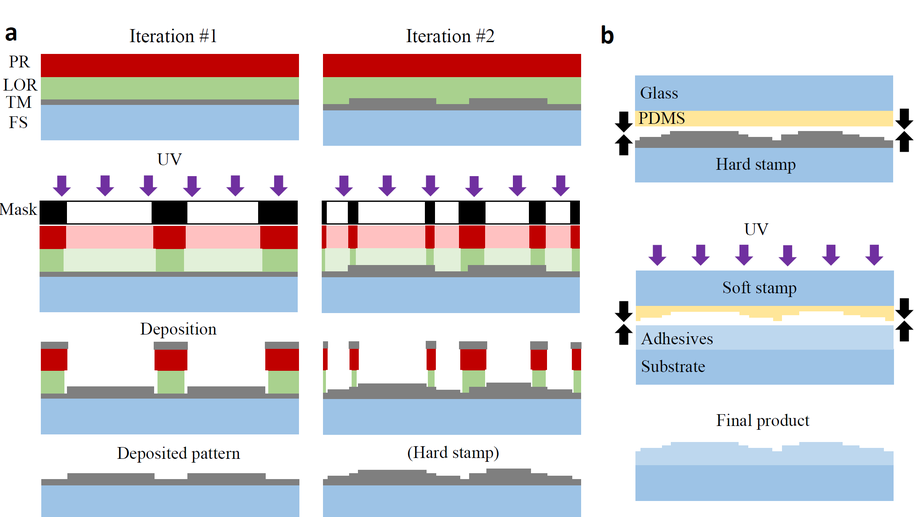
Etch-free additive lithographic fabrication methods for reflective and transmissive micro-optics
We propose an etch-free additive lithographic fabriction method for versatile reflective and transmissive DOEs.

Multispectral Illumination Estimation using Deep Unrolling Network
We propose a deep unrolling network to examine the problem of illumination spectra estimation in multispectral images.
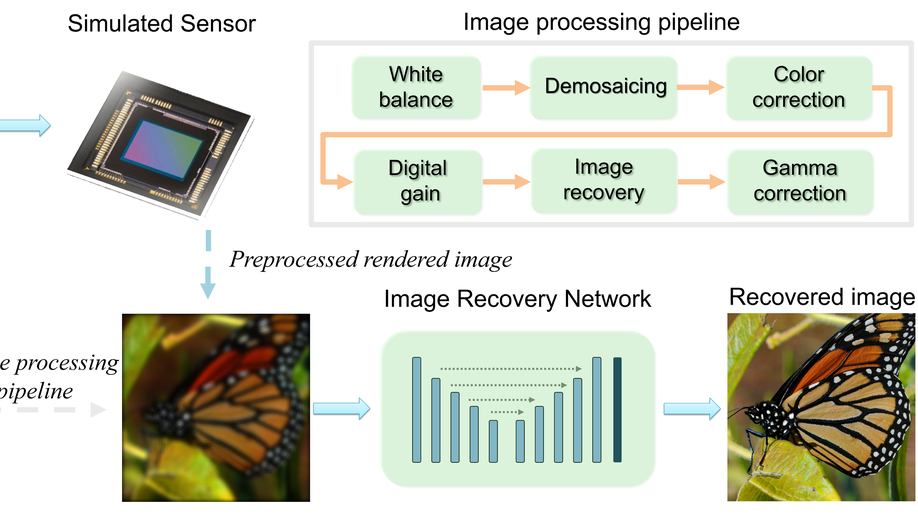
End-to-End Complex Lens Design with Differentiable Ray Tracing
We propose a general end-to-end complex lens design framework enabled by a differentiable ray tracing image formation model.
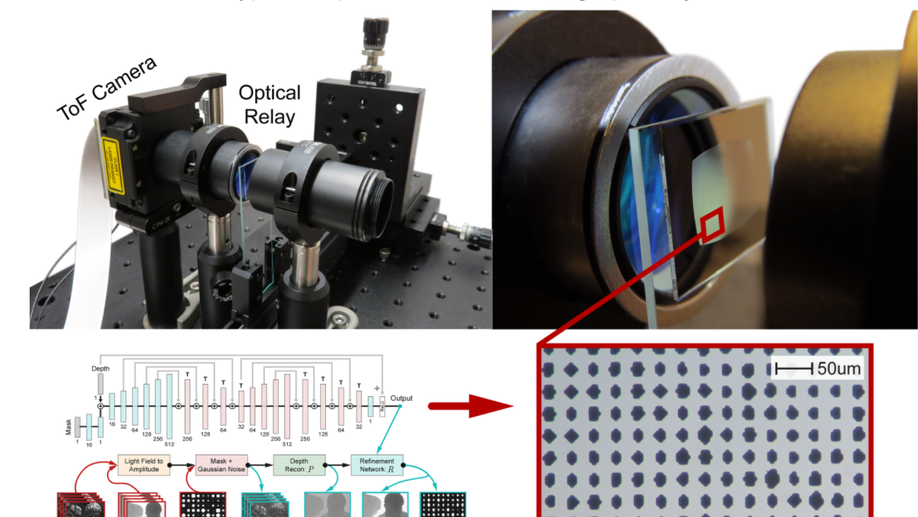
Mask-ToF: Learning Microlens Masks for Flying Pixel Correction in Time-of-Flight Imaging
We propose a mask-ToF method to mitigate the flying pixels in 3D imaging.

Transfer Deep Learning for Reconfigurable Snapshot HDR Imaging Using Coded Masks
We propose a joint design for snapshot HDR imaging with a spatially varying modulation mask.

Linear Polarization Demosaicking for Monochrome and Color Polarization Focal Plane Arrays
We propose a polarization demosaicking algorithm for both monochrome and colour DoFP cameras.
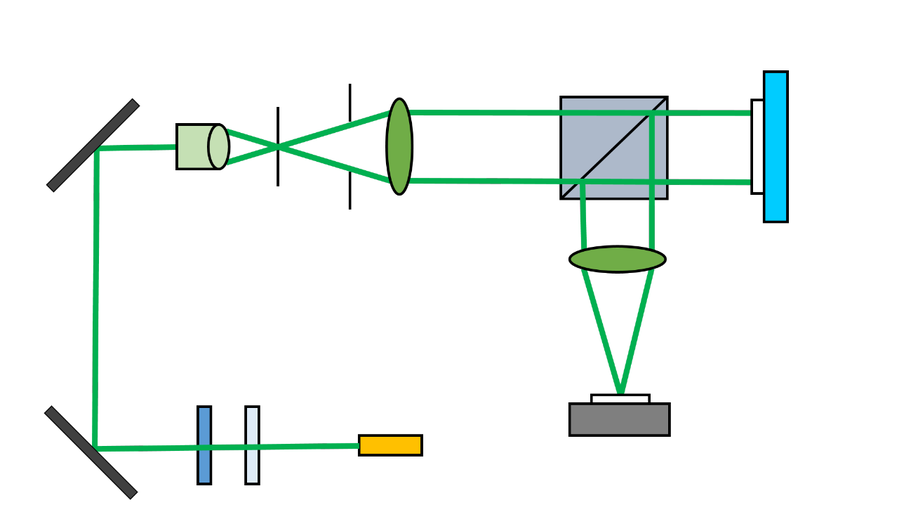
Robust statistical phase-diversity method for high-accuracy wavefront sensing
We porpose a combinatory method to improve phase retrieval performance.
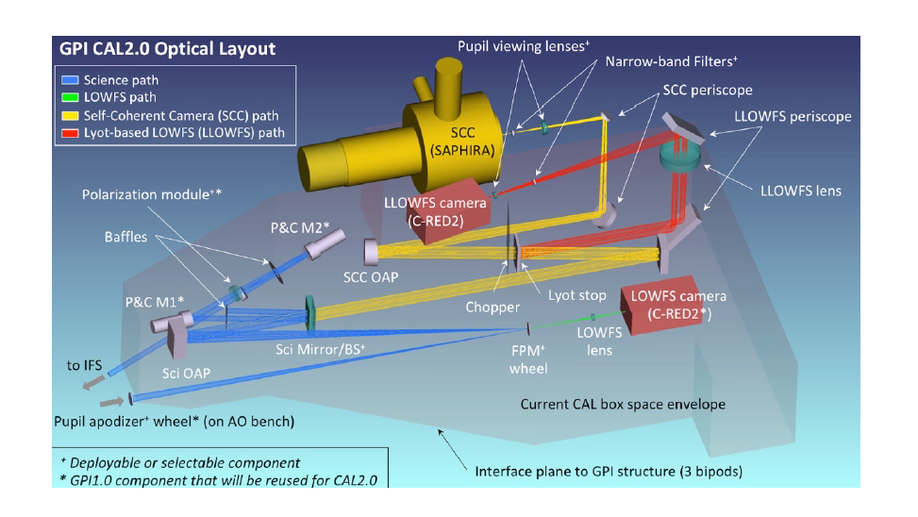
Upgrading the Gemini Planet Imager calibration unit with a photon counting focal plane wavefront sensor
We present a new second stage speckle-correction solution for the Gemini Planet Imager (GPI).
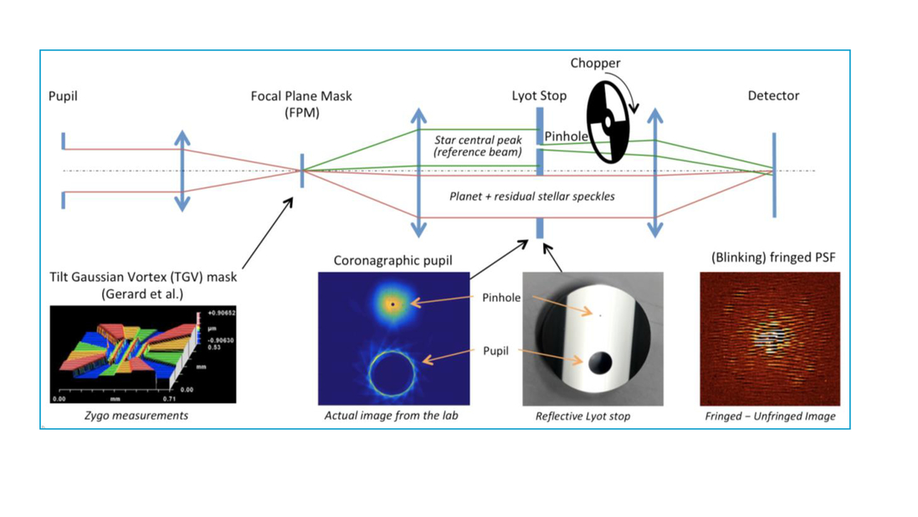
Optical design and preliminary results of NEW EARTH, first Canadian high-contrast imaging laboratory test bench
We present a bench optical design for the first Canadiana test-bed NEW EARTH.
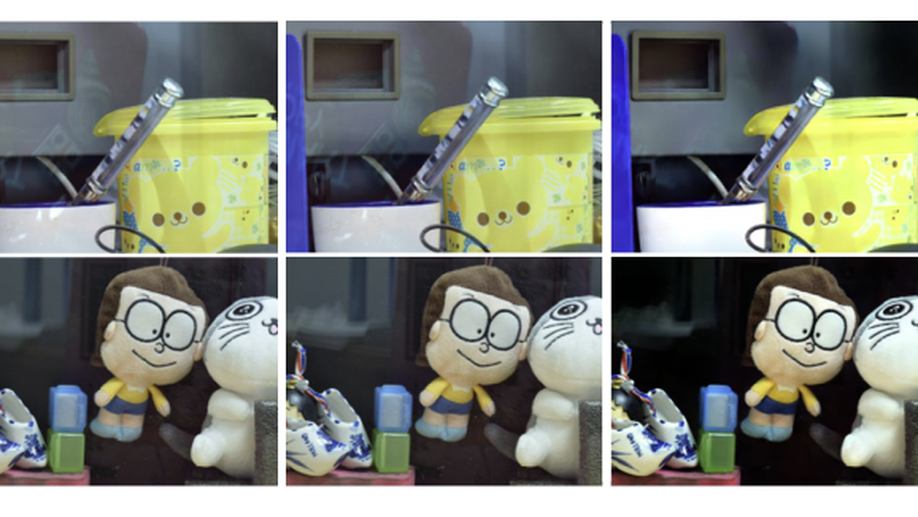

Reflection Removal via Realistic Training Data Generation
We present a valid polarization-based reflection contaminated image synthesis method.

Learning Rank-1 Diffractive Optics for Single-shot High Dynamic Range Imaging (oral)
We propose a method for snapshot HDR imaging by learning an optical HDR encoding with a DOE in a single image.
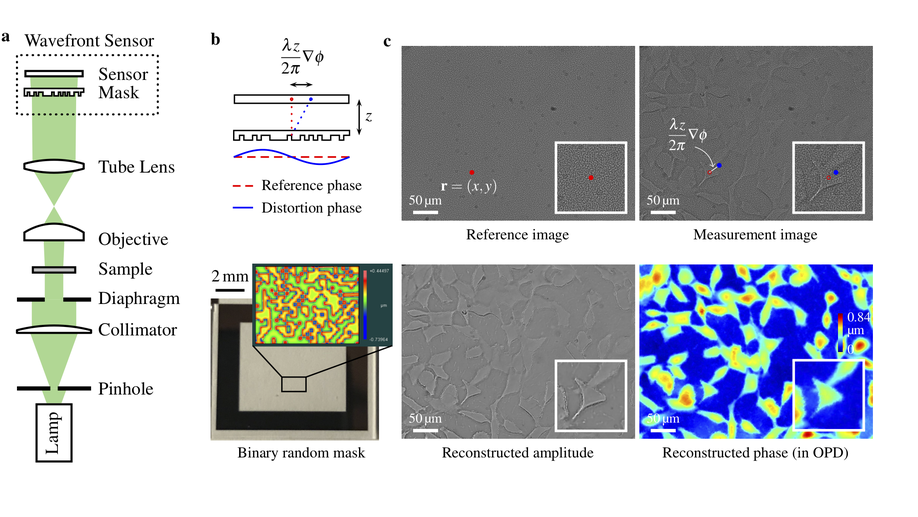
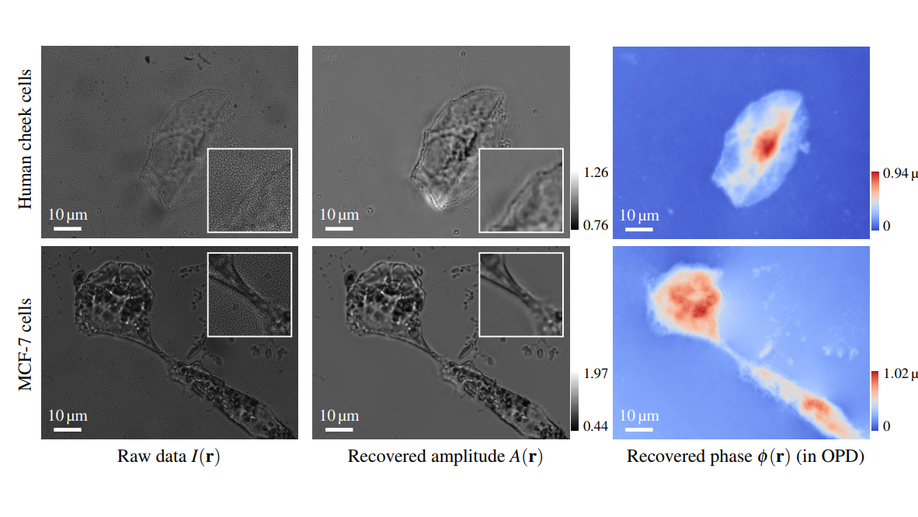
Quantitative Phase and Intensity Microscopy Using Snapshot White Light Wavefront Sensing
We demonstrate a quantitative imaging of phase and bright field amplitude using collimated white light illumination.
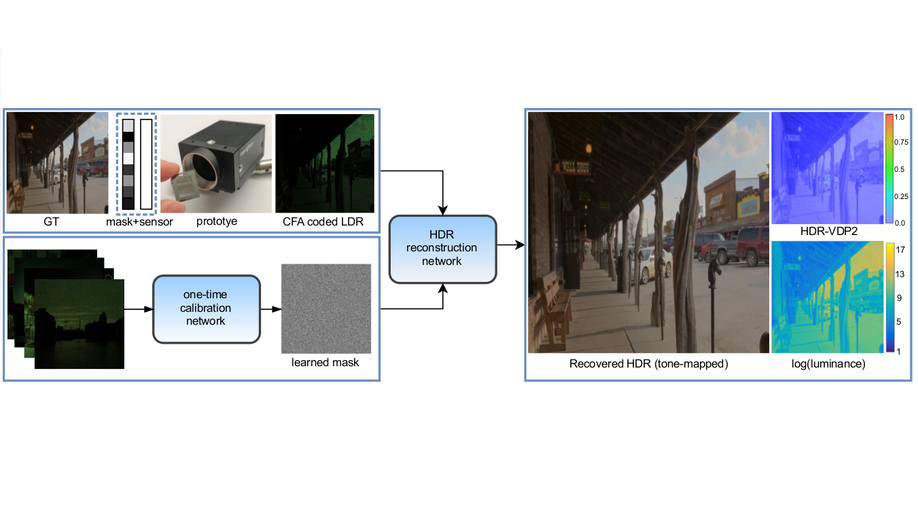
Reconfigurable Snapshot HDR Imaging Using Coded Masks and Inception Network
We propose an approach for HDR image reconstruction using a spatially-varying mask and an inception network.
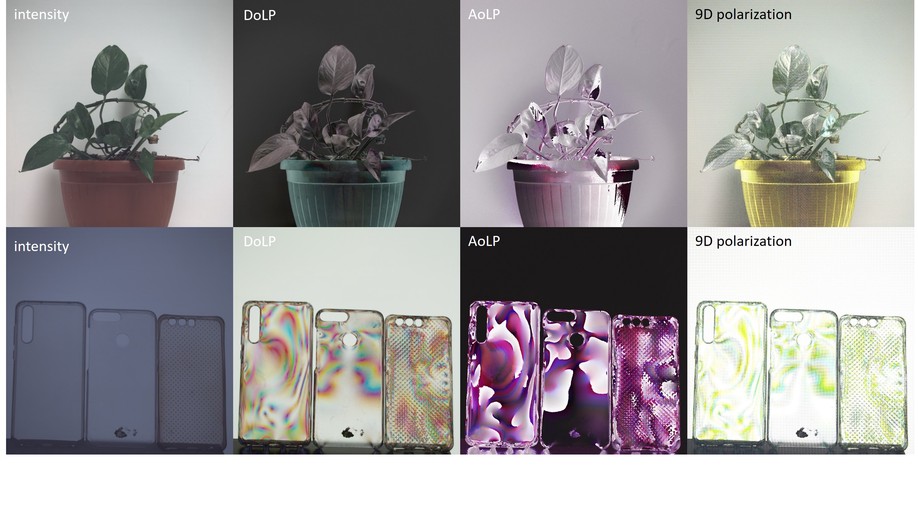
Polarization Demosaicking for Monochrome and Color Polarization Focal Plane Arrays
We propose a polarization demosaicking algorithm for both monochrome and color DoFP cameras.
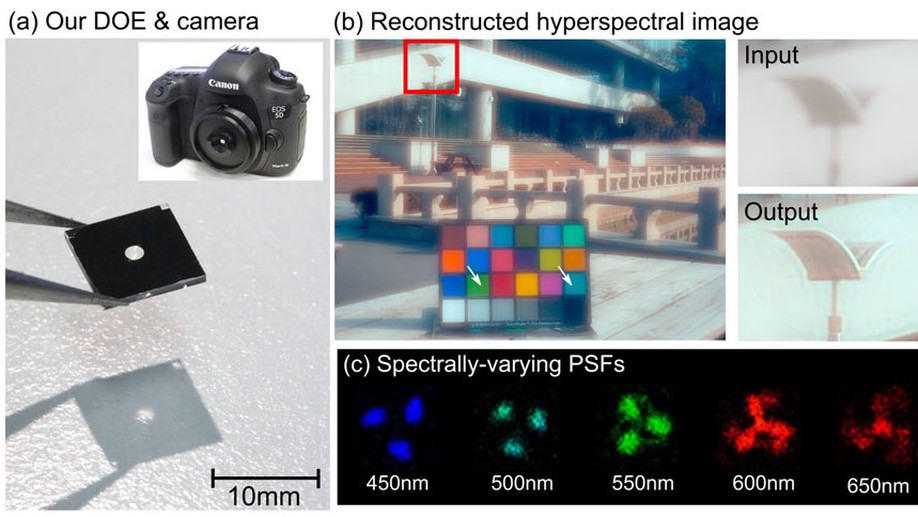
Compact Snapshot Hyperspectral Imaging with Diffracted Rotation
We propose a snapshot hyperspectral imaging system that employs a diffractive optical element and an end-to-end network.
A model for classical wavefront sensors and snapshot incoherent wavefront sensing
We propose a new formula to connect between slopes wavefront sensors and curvature sensors.
Megapixel Adaptive Optics: Towards Correcting Large-scale Distortions in Computational Cameras
We demonstrate an adaptive optics system for regular cameraswith unprecedented capability to sense and correct large distortions.
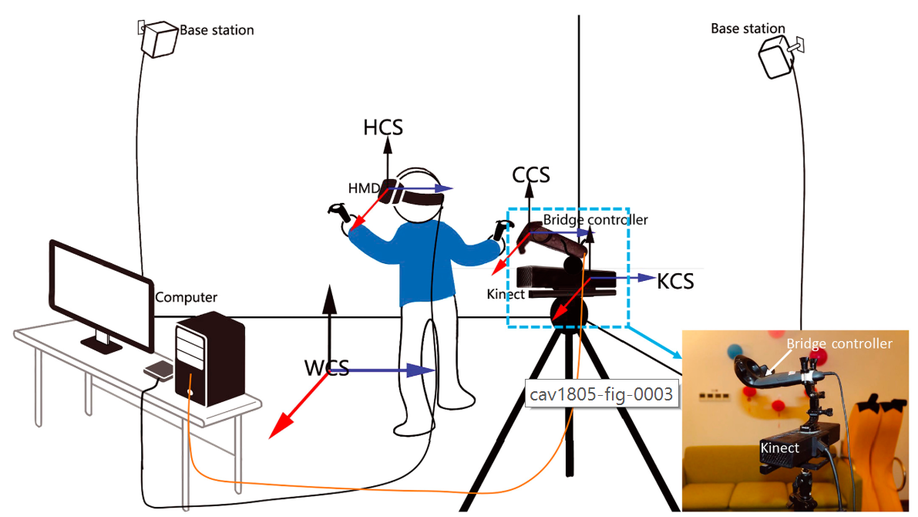
A shared augmented virtual environment for real‐time mixed reality applications
We propose a system to create high‐quality 1080p live MR footage, enabling realistic virtual experiences to be shared among a number of people.
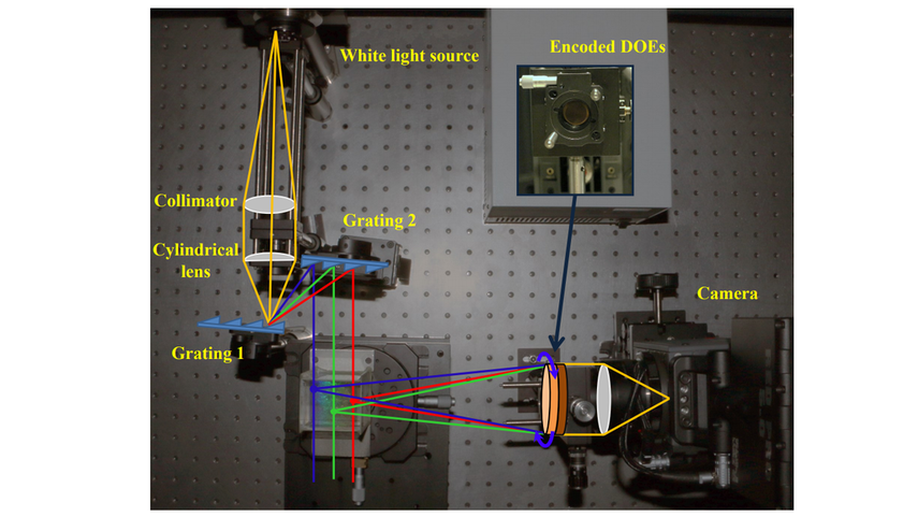
Reconfigurable Rainbow PIV for 3D Flow Measurement
We propose a reconfigurable rainbow PIV system that extends the volume size to a considerable range.
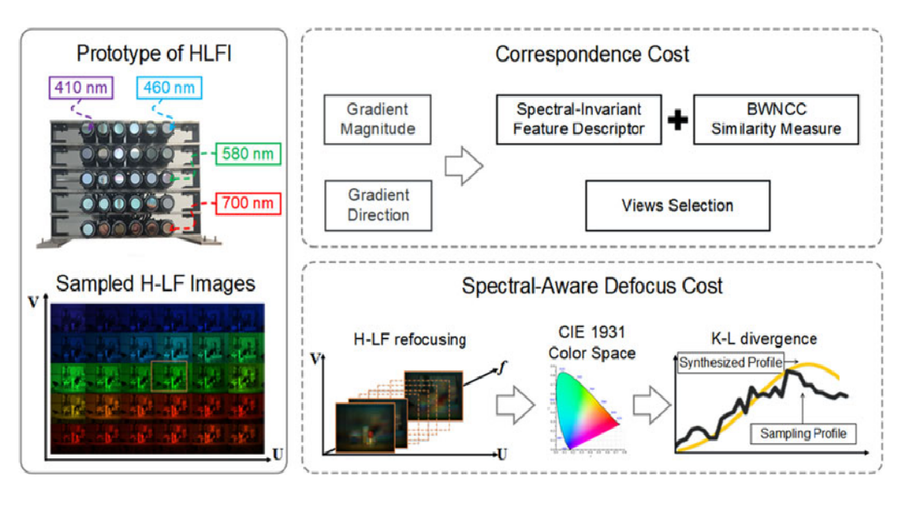
Hyperspectral light field stereo matching
We describe how scene depth can be extracted using a hyperspectral light field capture (H-LF) system.
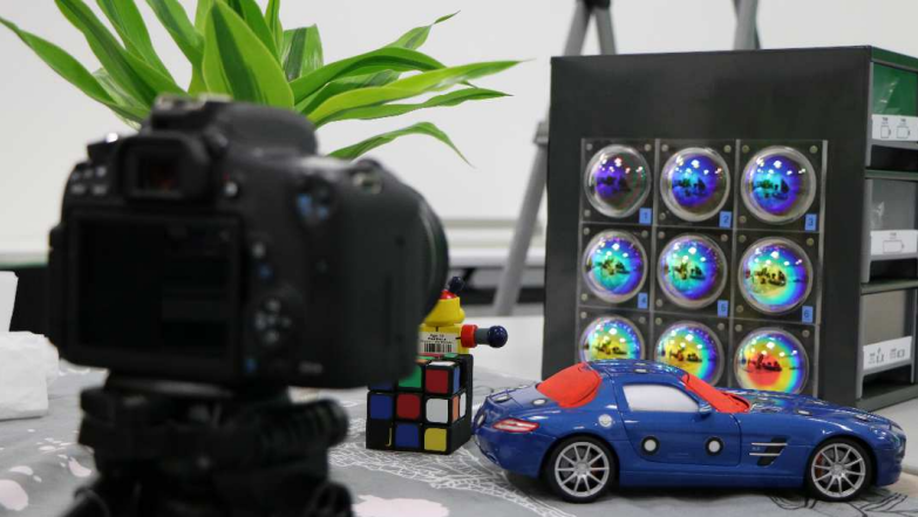

Catadioptric hyperspectral light field imaging
We present a single camera hyperspectral light field imaging solution with spectral coded catadioptric mirror arrays.
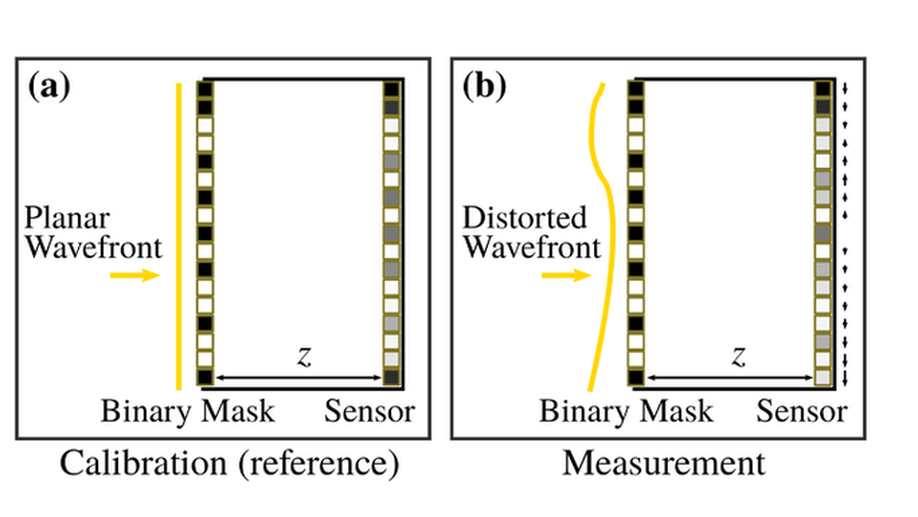
Ultra-High Resolution Coded Wavefront Sensor
We introduce a Coded Wavefront Sensor that provides high spatio-temporal resolution using a simple masked sensor, under white light illumination.
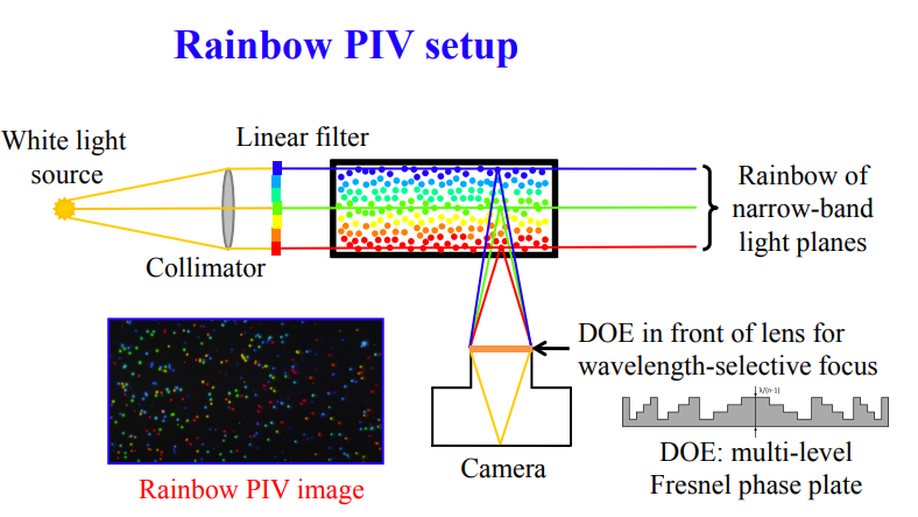
Rainbow Particle Imaging Velocimetry for Dense 3D Fluid Velocity Imaging
We demonstrate a 3D Particle Imaging Velocimetry method by employing a rainbow encoding and 3D optical flow decoding algorithm.
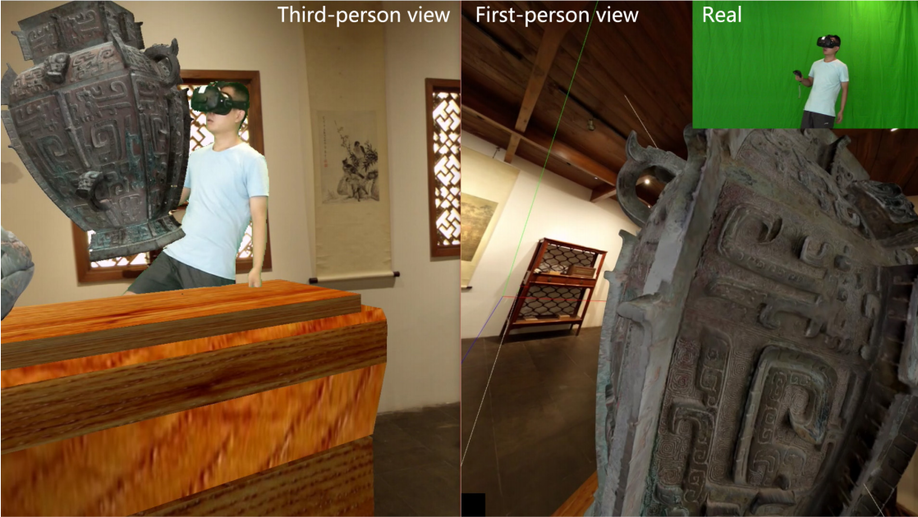

SAVE: shared augmented virtual environment for real-time mixed reality applications
We propose a mixed reality system that overlays the virtual world with real world objects captured by a Kinect depth camera.
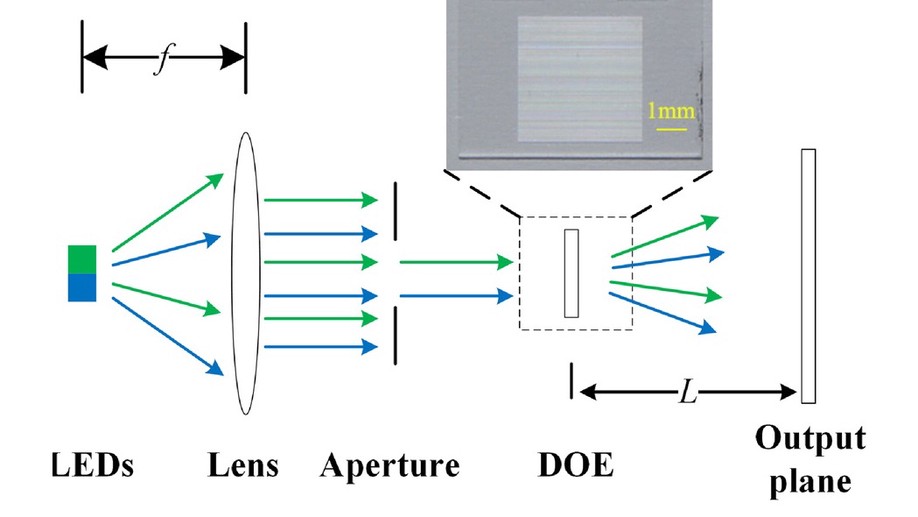
Beam shaping for multicolour light-emitting diodes with diffractive optical elements
We propose an improved particle swarm optimization method of ultra-thin diffractive optical elements design for multicolour beam shaping.
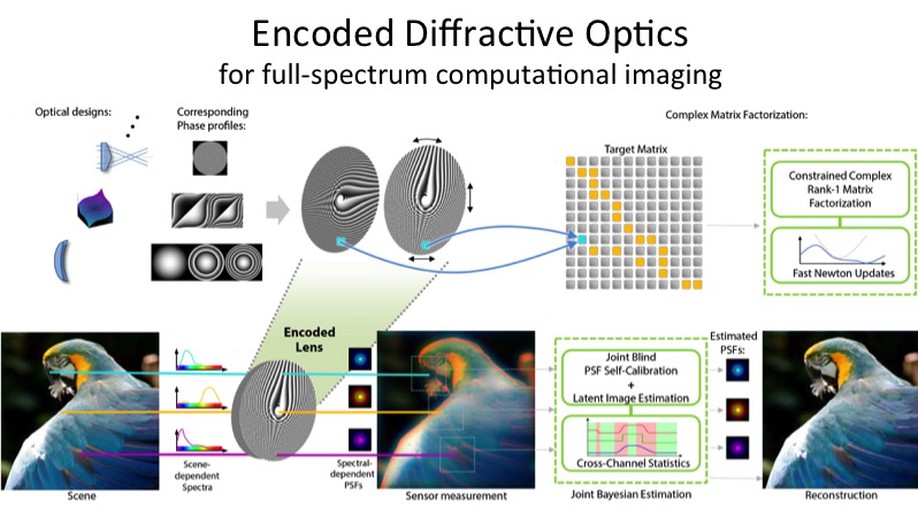
Encoded diffractive optics for full-spectrum computational imaging
We introduce numerically optimized encoded phase masks for focus and zoom through changes in the mechanical alignment.
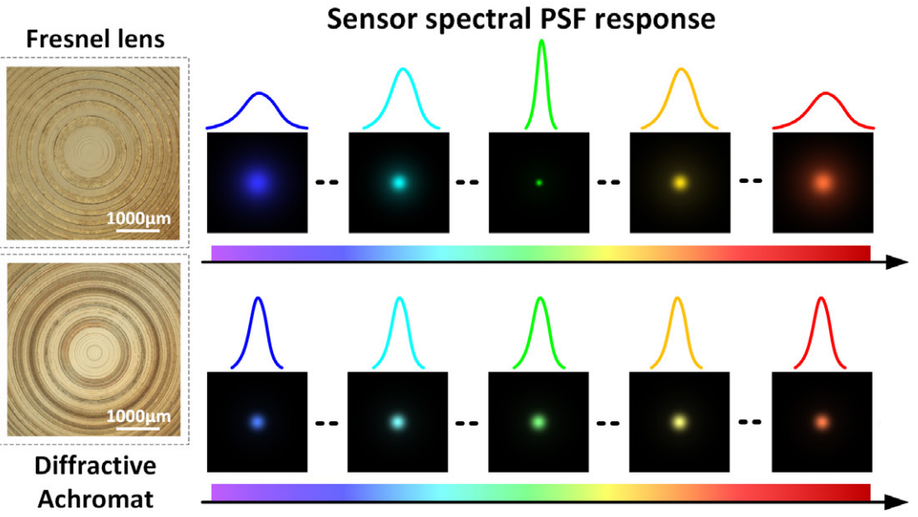
The diffractive achromat: full spectrum computational imaging with diffractive optics
We introduce a diffractive achromat based on computational optimization and a corresponding algorithm for correction of residual aberrations.
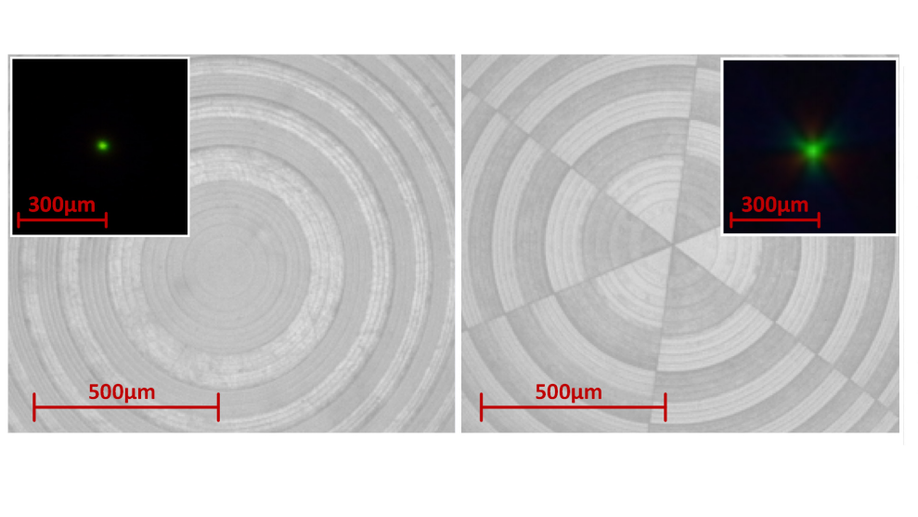
Computational imaging using lightweight diffractive-refractive optics
We jointly design lightweight diffractive-refractive optics and post-processing algorithms to enable imaging under white light illumination.