Abstract
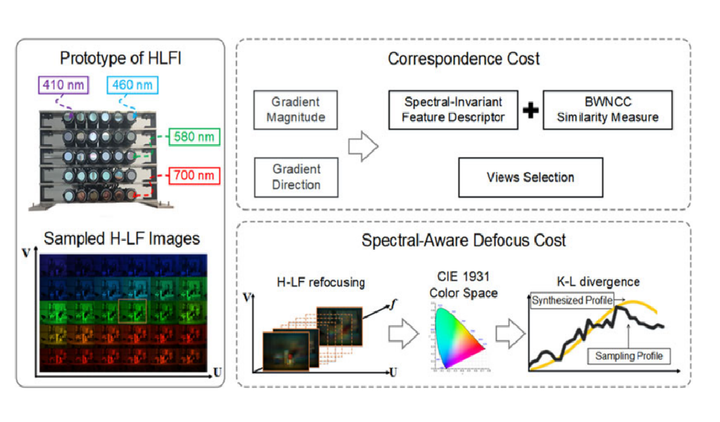
In this paper, we describe how scene depth can be extracted using a hyperspectral light field capture (H-LF) system. Our H-LF system consists of a 5×65×6 array of cameras, with each camera sampling a different narrow band in the visible spectrum. There are two parts to extracting scene depth. The first part is our novel cross-spectral pairwise matching technique, which involves a new spectral-invariant feature descriptor and its companion matching metric we call bidirectional weighted normalized cross correlation (BWNCC). The second part, namely, H-LF stereo matching, uses a combination of spectral-dependent correspondence and defocus cues. These two new cost terms are integrated into a Markov Random Field (MRF) for disparity estimation. Experiments on synthetic and real H-LF data show that our approach can produce high-quality disparity maps. We also show that these results can be used to produce the complete plenoptic cube in addition to synthesizing all-focus and defocused color images under different sensor spectral responses.
Citation
@article{zhu2018hyperspectral,
title={Hyperspectral light field stereo matching},
author={Zhu, Kang and Xue, Yujia and Fu, Qiang and Kang, Sing Bing and Chen, Xilin and Yu, Jingyi},
journal={IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence},
volume={41},
number={5},
pages={1131--1143},
year={2018},
publisher={IEEE}
}
All images are © IEEE 2019, reproduced here by permission of IEEE for your personal use. Not for redistribution.